What Is HERS?
The National Home Energy Ratings System (HERS)
In the 1992 Federal Energy Policy Act (“EPAct”) Congress mandated that the US Department of Energy and the US Department of Housing and Urban Development establish a national method to determine the energy performance of homes.
The purpose of this National Standard was so the energy performance of any home in any part of the country would be evaluated using the exact same methodology to give consumers a consistent "miles per gallon" type comparison of homes they are thinking of buying or building.
The National Home Energy Rating System (HERS) Standards came about from a national collaborative of energy, lending, utility, home building, realtor, and manufacturing stakeholders.
How the HERS Index Works
Step One
A Certified HERS Rater models a New or Existing Home in a RESNET Approved HERS Rating software program.
Step Two
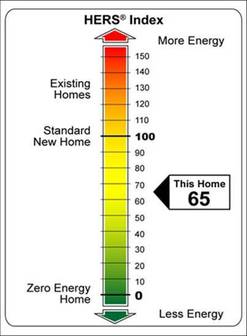
The HERS software compares the home being "Rated" to a computer simulation of that exact same house if it were built to roughly the 2007 National Energy Code. This computer model is called the "Reference Home" and would have a benchmark HERS Index score of 100.
Step Three
If the sum of ALL of the energy features of the home being Rated are BETTER than the Reference Home - the Rated Home will have a HERS Index LOWER than 100.
If the sum of ALL of the energy features of the home being Rated are WORSE than the Reference Home - the Rated Home will have a HERS Index HIGHER than 100.
The HIGHER a HERS Index is ABOVE 100 - the WORSE its energy performance.
The LOWER a HERS Index is BELOW 100 - The BETTER its energy performance.
A New Home built to IECC 2009 Energy Code will typically have a HERS Index in the 60-80 range.
A New Home built to IECC 2012 Energy Code will typically have a HERS Index in the 40-60 range.
A New Home with a HERS Index of Zero (0) or lower would be a Net Zero Energy Home.